|
Composition | Health Benefits | Mediterranean Diet
Olive oil is an excellent alternative to butter or margarine for use in food preparation or for use as a condiment. It enhances the taste of many foods and it has proven health benefits. Because olive oil is so flavorful, less is required to add flavor to food. This reduces the calories and the total fat content of food prepared or served with olive oil compared to food prepared with other less flavorful oils.
Composition
Olive oil contains a high percentage of monounsaturated fat, which is healthier than the polyunsaturated fats found in corn oil and much healthier than the saturated fats found in butter. Because olive oil is vegetable based, it contains no cholesterol.
| Types of Fat Structures |
| Unsaturated Fats |
| Polyunsaturated Fat |
The main sources of polyunsaturated fats are seeds, nuts, grains, and vegetables. Polyunsaturated fat is usually in a liquid state at room temperature and also when chilled. It lowers the overall cholesterol level, but it also reduces HDL or good cholesterol. Recommended daily allowances of polyunsaturated fats should be part of a balanced diet, but some tests have shown that high consumption may actually be damaging to the digestion and nervous systems, so moderation is the key for a balanced and healthy diet.
Omega-3 fatty acid is a type of polyunsaturated fat that is especially healthy. Omega-3 fatty acids help to reduce the risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure, guard against plaque buildup in the arteries, and aid in brain development. It is found in some plant oils and in the tissues of all sea creatures. Among the plant oils rich in omega-3 fatty acids are flax seed, canola, and soybean oil. Fish that are particularly high in omega-3 are sardines, herring, tuna, and salmon. |
| Monounsaturated Fat |
Most animal and vegetable fats contain monounsaturated fat, but in varying quantities. It is usually in liquid form at room temperature, but it may begin to solidify if it is chilled. Monounsaturated fat is the most desirable type of fat in the diet because it helps to decrease the LDL (bad) cholesterol in the blood and helps to increase the HDL (good) cholesterol. Good sources of monounsaturated fat are olive oil, macadamia nut oil, canola oil, peanut oil, and most nuts. |
| Saturated Fats |
| Saturated Fat |
Animal meats, butter, whole milk, and some tropical plant oils, such as palm and coconut, are the main sources of saturated fat, which is the least healthy type of fat. Saturated fat raises the level of LDL (bad) cholesterol, which causes numerous health problems if consumed in large quantities. Most saturated fats are solid at room temperature. |
| Trans-fatty Acid |
Trans-fatty acid, also known as trans-fat, is formed when hydrogen is added to vegetable oil in order to change the liquid oil into a solid at room temperature. This process is known as hydrogenation, which also transforms the unsaturated fats of the liquid oils into saturated fat. Like saturated fat, trans-fat may raise blood cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart related diseases. Many shortenings, margarine, and commercially baked goods are high in trans-fatty acids.
One advantage that hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated fats have is that they are less likely to turn rancid, which is very beneficial to the commercial food industry in creating foods with a longer shelf life. As with any type of food containing saturated fat, foods containing hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated fat should be enjoyed in moderation in order to maintain a balanced and healthy diet. |
The table below shows how olive oil compares with other popular oils in fat composition.
|
Type of Oil |
Monounsaturated |
Polyunsaturated |
Saturated |
| Macadamia Nut Oil |
83% |
3% |
14% |
| Olive Oil |
77% |
9% |
14% |
| Canola Oil |
62% |
32% |
6% |
| Peanut Oil |
49% |
33% |
18% |
| Corn Oil |
25% |
62% |
13% |
| Soybean Oil |
24% |
61% |
15% |
| Sunflower Oil |
20% |
69% |
11% |
| Safflower Oil |
13% |
77% |
10% |
Regardless of the type or grade, olive oil contains 120 calories per tablespoon. In fact, all edible food oils contain about 120 calories per tablespoon. When used for cooking, the healthy aspects of olive oil do not change as the oil is heated.
Olive oil is good source of the antioxidant, vitamin E. It contains 1.6 mg. of vitamin E per tablespoon, which is 8% of the recommended daily allowance.
Health Benefits
Olive oil has been linked to the following health benefits:
- Lowering the risk of heart disease
- Reduction in the level of LDL (bad) cholesterol
- Lowering of blood pressure
- Decrease in blood sugar levels
- Increase in the absorption of several vitamins including A, D, E, and K
- Stimulation of the gall bladder to secrete bile, which helps to prevent gallstones
- Promotes cellular growth, speeds healing, and helps the metabolism
Olive oil is also beneficial for the skin and hair. Overly dry skin or sun damaged skin can be soothed with the application of olive oil. Some people apply olive oil to the skin to prevent wrinkles, although there is no scientific evidence to support this. Olive oil promotes shiny and full-bodied hair and a healthy scalp.
Some scientific studies have indicated that olive oil may reduce some of the effects of aging. It helps with digestion and the absorption of nutrients, which tends to slow as people age. It helps to maintain healthy bones and prevents calcium loss. The natural antioxidants in olive oil may even help to maintain mental faculties for a longer period.
In spite of the health benefits of olive oil, it should not be overused, because like all other edible oils, it is a high source of calories. One tablespoon of olive oil contains about 120 calories, but because it is so flavorful, a little can go a long way when used as a cooking oil, a salad dressing, or condiment.
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is based on the consumption of plenty of fruits and vegetables, grains, beans, nuts, cheese, fish, poultry, and olive oil. Some of the lowest rates of heart disease in the world occur in Mediterranean countries, even though the diet contains as much fat as the U.S. diet. Most of the fat, however, is in the form of heart-healthy monounsaturated fat found in olive oil and most nuts and omega-3 fatty acids found in many fish and grains. In general, the diet places more emphasis on foods from plant sources than from animal sources. The American Heart Association has found that a diet rich in these foods may help to prevent cardiovascular disease.
|
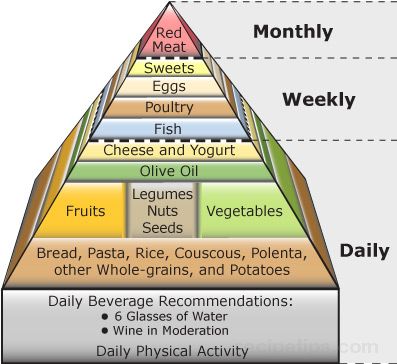
Mediterranean Diet Pyramid
The Mediterranean diet pyramid is based on the traditional diets of people in Greece, Crete, and southern Italy in the early 1960's. During that time, the incidence of chronic disease in the region was among the lowest in the world and the life expectancy was among the highest in spite of the limited medical resources that were available at the time. Current scientific research is proving what has been suspected for many years - that the Mediterranean diet, in conjunction with daily physical activity, is synonymous with good health.
The Mediterranean diet features a greater emphasis on foods obtained from plant sources. The total fat intake is about the same as the traditional food guide pyramid, but because of the high consumption of olive oil, most of the fat is in the form of monounsaturated fat, which has proven health benefits.
It is also interesting to note that moderate wine consumption at mealtime is recommended for adults as part of a healthy diet. Scientific studies have suggested that 1 or 2 small glasses of wine (especially red wine) per day may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems because of the antioxidants contained in the wine. However, overindulgence will have the opposite effect and may lead to other serious health problems. |
 |
|
USDA Food Guide Pyramid
The USDA food guide pyramid provides an outline of the types of foods that should be consumed daily for proper nutrition. Foods should be selected that are low in saturated fat and calories in order to maintain a healthy weight while providing the required nutrients necessary for overall health. |
 | |

