Specifics of the Mediterranean Diet Plan
Food Guide Pyramid for the Mediterranean Diet Plan
|
The updated food guide pyramid, which outlines a diet developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), is one of the best plans for maintaining a healthy balanced diet. There are, however, other diet plans that are equally beneficial in maintaining proper nutrition. One such plan, which has been proven to be healthful, is the "Mediterranean Diet." It is based on the types of foods that for centuries have been consumed by the people who live in the countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea.
 In general, the Mediterranean diet emphasizes the consumption of foods from plant sources and foods that are not highly processed. The American Heart Association has found that a diet rich in these types of foods may help to prevent cardiovascular disease. Some of the lowest rates of heart disease in the world occur in Mediterranean countries, even though the diet contains as much fat as the U. S. diet; however, most of the fat in the Mediterranean diet is in the form of heart-healthy monounsaturated fat found in olive oil and in most nuts. Also beneficial is omega-3 fatty acid, found in some fish and grains, which is consumed in larger quantities in the Mediterranean region than in the United States. In general, the Mediterranean diet emphasizes the consumption of foods from plant sources and foods that are not highly processed. The American Heart Association has found that a diet rich in these types of foods may help to prevent cardiovascular disease. Some of the lowest rates of heart disease in the world occur in Mediterranean countries, even though the diet contains as much fat as the U. S. diet; however, most of the fat in the Mediterranean diet is in the form of heart-healthy monounsaturated fat found in olive oil and in most nuts. Also beneficial is omega-3 fatty acid, found in some fish and grains, which is consumed in larger quantities in the Mediterranean region than in the United States.
|
Specifics of the Mediterranean Diet Plan
Foods Included in the Mediterranean Diet Plan
Whole-grains and whole-grain products, especially whole-grain breads; fruits and vegetables; legumes, nuts, and seeds; dairy products, such as cheese and yogurt; fish; poultry; and olive oil, are the types of foods that form the basis of the Mediterranean diet. Red meats and homemade sweets are occasionally eaten, but highly refined processed foods are seldom consumed. The unhealthy practice of snacking on junk foods—commercially produced chips, crackers, cookies, cakes, candies, and sodas—is rare among the people of the Mediterranean region who have eaten fresh, unprocessed food products all of their lives. An uncommon practice is to serve sweet desserts after evening meals: Fruits, yogurt, and cheeses are most often served as a dessert course in the region, especially in the non-European Mediterranean countries. |
Typical Foods of the Mediterranean Diet
 
Whole-grains and Whole-grain Breads
 
Fruits and Vegetables
 
Legumes, Nuts, and Seeds
  
Cheese, Yogurt, and Olive Oil
 
Fish and Poultry
|
|
Some of the Foods that are Occasionally Eaten
 
Red Meat and Homemade Sweets
|
|
The Types of Highly Refined Processed Foods that are Seldom Eaten
 
 
Commercially Produced Chips, White Bread, Cookies, and Candy
|
The Importance of Olive Oil in the Mediterranean Diet
 Olive oil is among the most important foods of the Mediterranean diet. It is used as the primary cooking medium (butter is seldom used) and as the chief condiment: Breads are dipped into it; vegetables and salads are dressed with it; and the flavor of grains, fish, and poultry is enhanced with it. Olive oil is among the most important foods of the Mediterranean diet. It is used as the primary cooking medium (butter is seldom used) and as the chief condiment: Breads are dipped into it; vegetables and salads are dressed with it; and the flavor of grains, fish, and poultry is enhanced with it.
Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fat, which is a "good" fat, because it helps to decrease the LDL (bad) cholesterol in the blood and helps to increase the HDL (good) cholesterol. It is usually in liquid form at room temperature, but it may begin to solidify when it is chilled. Most animal and vegetable fats contain monounsaturated fat, but in varying quantities. Olive oil has the highest percentage (about 77%) of monounsaturated fat among commonly used oils. (Macadamia nut oil actually has the highest percentage (about 83%) of monounsaturated fat of any edible oil, but it is expensive and it is not as commonly used in cooking as other oils.)
Although olive oil has proven health benefits, it is still 100% fat, and most doctors and nutritionists believe that people should limit their usage of fat. Like all other plant oils, olive oil has about 120 calories per tablespoon, so in spite of its favorable nutritional profile, consuming it in large quantities may contribute to weight gain. As with any food, the key when using olive oil is to practice moderation, because as we all know, too much of a good thing can result in weight gain, which can lead to a host of medical problems. |
Food Guide Pyramid for the Mediterranean Diet Plan
|
The Mediterranean diet pyramid is based on the traditional diets of people in Greece, Crete, and southern Italy in the early 1960's. During that time, it was discovered that the incidence of chronic disease in the region was among the lowest in the world, and the life expectancy was among the highest in spite of the limited medical resources that were available in the region at the time. Current scientific research is proving what has been suspected for many years—the Mediterranean diet, in conjunction with daily physical activity, is synonymous with good health.
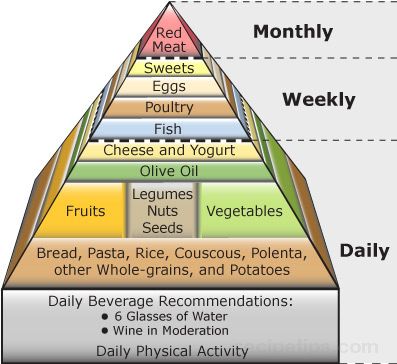
Foods that should be eaten daily are shown in the lower levels of the Mediterranean diet pyramid while foods that should be consumed less frequently, perhaps weekly or monthly, are shown in the middle and upper levels of the pyramid. Although the Mediterranean diet features a greater emphasis on foods obtained from plant sources, the total fat intake is about the same as the traditional USDA food guide pyramid. This is because of the high consumption of olive oil, which, as noted previously, is in the form of healthful monounsaturated fat.
 It is also interesting to note that moderate wine consumption at mealtime is recommended for adults as part of a healthy diet. There have been a number of scientific studies, including studies in the United States, that have suggested that one or two small glasses of wine (especially red wine) per day may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems: The antioxidants contained in the wine provide this benefit; however, overindulgence will have the opposite effect and may lead to other serious health problems. It is also interesting to note that moderate wine consumption at mealtime is recommended for adults as part of a healthy diet. There have been a number of scientific studies, including studies in the United States, that have suggested that one or two small glasses of wine (especially red wine) per day may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems: The antioxidants contained in the wine provide this benefit; however, overindulgence will have the opposite effect and may lead to other serious health problems.
It should also be noted that although mounting evidence is confirming the health benefits of wine (when used in moderation); there has not been a universal acceptance of this. Some doctors, especially in the United States, are reluctant to accept this is a prescription for good health, perhaps because abuse is such a widespread problem. | |

 In general, the Mediterranean diet emphasizes the consumption of foods from plant sources and foods that are not highly processed. The American Heart Association has found that a diet rich in these types of foods may help to prevent cardiovascular disease. Some of the lowest rates of heart disease in the world occur in Mediterranean countries, even though the diet contains as much fat as the U. S. diet; however, most of the fat in the Mediterranean diet is in the form of heart-healthy monounsaturated fat found in olive oil and in most nuts. Also beneficial is omega-3 fatty acid, found in some fish and grains, which is consumed in larger quantities in the Mediterranean region than in the United States.
In general, the Mediterranean diet emphasizes the consumption of foods from plant sources and foods that are not highly processed. The American Heart Association has found that a diet rich in these types of foods may help to prevent cardiovascular disease. Some of the lowest rates of heart disease in the world occur in Mediterranean countries, even though the diet contains as much fat as the U. S. diet; however, most of the fat in the Mediterranean diet is in the form of heart-healthy monounsaturated fat found in olive oil and in most nuts. Also beneficial is omega-3 fatty acid, found in some fish and grains, which is consumed in larger quantities in the Mediterranean region than in the United States.
















 Olive oil is among the most important foods of the Mediterranean diet. It is used as the primary cooking medium (butter is seldom used) and as the chief condiment: Breads are dipped into it; vegetables and salads are dressed with it; and the flavor of grains, fish, and poultry is enhanced with it.
Olive oil is among the most important foods of the Mediterranean diet. It is used as the primary cooking medium (butter is seldom used) and as the chief condiment: Breads are dipped into it; vegetables and salads are dressed with it; and the flavor of grains, fish, and poultry is enhanced with it.
 It is also interesting to note that moderate wine consumption at mealtime is recommended for adults as part of a healthy diet. There have been a number of scientific studies, including studies in the United States, that have suggested that one or two small glasses of wine (especially red wine) per day may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems: The antioxidants contained in the wine provide this benefit; however, overindulgence will have the opposite effect and may lead to other serious health problems.
It is also interesting to note that moderate wine consumption at mealtime is recommended for adults as part of a healthy diet. There have been a number of scientific studies, including studies in the United States, that have suggested that one or two small glasses of wine (especially red wine) per day may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems: The antioxidants contained in the wine provide this benefit; however, overindulgence will have the opposite effect and may lead to other serious health problems.